Space-Based Solar Power: Borrowing Sunlight from the Sky
Have you ever thought that the sunlight we bask in every day could one day "fly" into space to provide an endless supply of energy for Earth? It sounds like something out of a science fiction novel, but in reality, space-based solar power is precisely what scientists are striving to achieve. This technology could not only solve our energy problems but also make solar power generation independent of daytime and weather conditions.
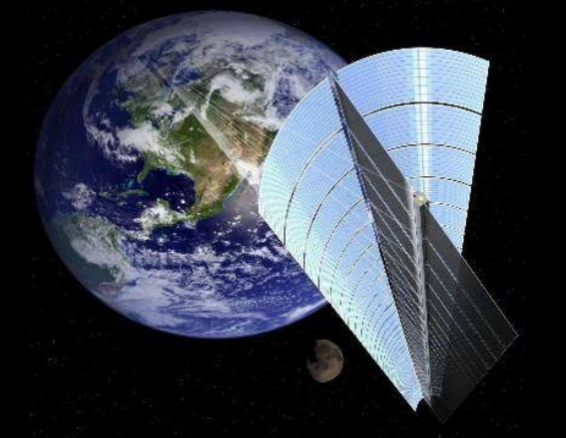

First, let’s talk about how this technology works. Most of us are familiar with terrestrial solar power. Each year, the amount of energy radiated to Earth by the sun is enough to meet our needs for centuries. However, the problem lies in the fact that solar power can only be utilised during the day and is limited by weather and geography. Thus, while solar power appears to be environmentally friendly, it’s not always reliable in areas with frequent cloudy days or at night. Space-based solar power, on the other hand, works differently. Simply put, it involves deploying solar collectors in space, where they can continuously and unobstructedly receive solar energy without interference from the Earth’s atmosphere. The collected solar energy is then converted into microwaves or lasers, transmitted to Earth via beams, and subsequently converted into electricity using specialised receiving equipment. Sounds a bit like "beaming" sunlight back down, doesn’t it? Indeed, that’s the core principle of space-based solar power.
So, why move solar power to space? On Earth, sunlight is limited by absorption from air and clouds, especially on overcast days with weaker light, which significantly reduces solar energy efficiency. In space, however, there are no clouds or atmospheric barriers. Sunlight can reach the collectors almost without restriction. Think of it as having all the energy from sunlight seamlessly entering your "stomach", offering more efficient energy intake.
Moreover, space solar power systems aren’t affected by the day-night cycle. Terrestrial solar power systems can only operate for half the day—during daylight hours. In contrast, space-based solar collectors can receive energy from the sun continuously, working 24 hours a day. This means solar power can be generated in space round the clock, regardless of whether it’s day or night on Earth.
Of course, while this sounds "too good to be true", there are significant challenges to commercialising space-based solar power. First is the issue of how to safely and effectively launch these systems into space. Despite advancements in space technology, sending large solar collection systems into orbit remains a massive engineering feat. Then there’s the question of how to reliably transmit this energy back to Earth. The precision of delivering electricity from space to specific locations on Earth presents a significant technical challenge. Additionally, the cost factor cannot be ignored. Just like preparing an extravagant meal with expensive ingredients and complex preparation, the cost of space-based solar power is high. Each launch, maintenance operation, and system operation requires substantial financial and technical investment. As a result, current space solar projects remain in experimental and research stages, with large-scale applications still a ways off.
However, imagine if this technology matures—our energy sources would no longer rely on coal, oil, or other resources and wouldn’t be constrained by weather or seasons. Picture a future where all the electricity in homes and factories is supplied by "sunlight beamed from space". This wouldn’t just be an environmentally friendly choice but also an infinitely sustainable energy solution. Doesn’t it feel like science fiction is becoming a reality?
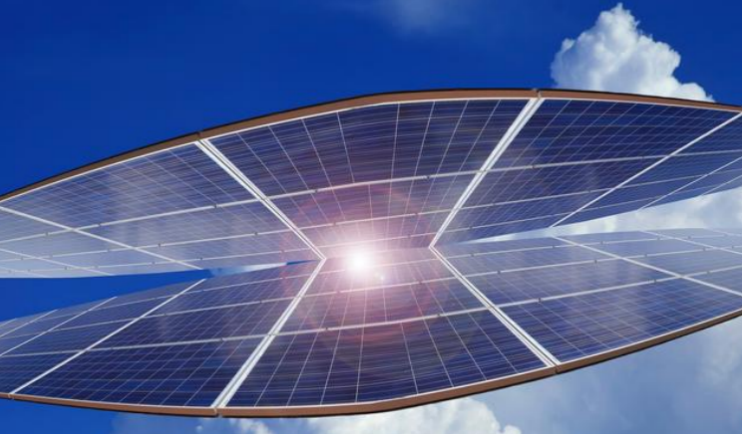

In summary, space-based solar power is an innovative yet challenging technology. While high costs and technical hurdles currently prevent widespread adoption, this technology undoubtedly represents a promising "blue ocean" for future energy solutions. As scientists continue to overcome challenges, it’s likely that in the not-too-distant future, we’ll be able to borrow endless sunlight from space to solve Earth’s energy problems. When that day comes, concerns about power shortages will become a thing of the past as the sun "takes to the skies" to provide us with constant support.
(Writer:Ciki)